
Table of Contents (Start)
SevOne Installation Guide - Virtual Appliance
SevOne Documentation
All SevOne user documentation is available online from the SevOne Support website.
-
Enter email address and password.
-
Click Login.
-
Click the Solutions icon.
© Copyright 2015, SevOne Inc. All rights reserved. SevOne, SevOne PAS, SevOne DNC, SevOne PLA, Deep Flow Inspection, and Rethink Performance are either registered trademarks or trademarks of SevOne Inc. Other brands, product, service and company names mentioned herein are for identification purposes only and may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Create Support Account
SevOne support is only a phone call away - +1-302-319-5400. Perform the following steps to create a user account to enable SevOne Support Engineers to provide support services.
-
In the address field on your web browser enter www.sevone.com/support and press Enter.
-
Click Login to display the SevOne Support Login page.
-
In the Create New Account section, enter the following information.
-
Your Full Name
-
Email Address
-
Phone Number
-
Company
-
-
Click Create Account.
-
Your account is created instantly and SevOne Support reviews the account validity within the next business day.
Prerequisites and Hardware Requirements
This document describes the installation of a SevOne virtual appliance. Virtual appliances can be a SevOne Performance Appliance Solution (vPAS) that runs the SevOne Network Management Solution (NMS) software or a SevOne Performance Log Appliance (vPLA) that runs the SevOne PLA software. Screen captures and workflows in this document describe SevOne NMS version 5.4.x and SevOne PLA version 2.0.1.
vPAS Host System Requirements
-
Intel-VT or AMD-V CPU extensions
-
VMware ESXi v5.0+
-
Does not run on VMware Workstation / VMware Player
|
Hardware Component |
vPAS 5K |
vPAS 20K |
vPAS 100K |
vPLA |
|
CPU |
2 vCPU |
8 vCPU |
8 vCPU |
2 vCPU |
|
Memory |
4GB |
16GB |
128GB |
1 GB Memory for every GB of daily uncompressed log data |
|
Hard Drives |
150GB / 600GB |
600GB / 600GB |
3000GB / 3000GB 1K IOPS Average over two hours |
Minimum free hard drive space 100 GB storage for every GB of daily uncompressed log data. |
|
Other |
|
|
|
64-bit Infrastructure IP address assigned by DHCP by default |
Used hard drive space vs Provisioned Capacity. Virtual machines are thin provisioned and consumption used space is based on 1 year of polling at 5 minute intervals.
VMware Initial Setup Best Practices
-
The SevOne .ova image file contains a Gentoo package app-emulation/vmware-tools to provide emulation for what vCenter and the ESX need to get from the VM. This package provides a set of utilities and drivers to help you improve the performance and management of virtual machines.
-
VMware Tools include the VMXNET3 network driver. The VMXNET3 adapter is a virtualized Network Interface Card that offers better performance and should be used for the vPAS 100K.
-
Turn on Storage I/O Monitoring in vCenter for all data stores used by the appliance to diagnose performance issues.
-
Ensure that hyperthreading is enabled by default in the virtual data center. Hyperthreading is enabled or disabled in the BIOS when the system is booted.
-
Ensure adequate CPU and memory allocation as described earlier in this document. Do not inadvertently limit CPU or memory and ensure that the Unlimited check box is selected.
For a physical system, the concept of a CPU is easy term to understand. However, in the virtualized space it is difficult to determine how many cores a CPU has and whether hyperthreading is turned on. One way to normalize the values you should use to plan your virtual environment is to use the SPECint benchmark published by SPEC. SPEC breaks out CPU performance metrics for:
-
CPU Speed (cint)
-
CPU Throughput (rint)
The cint performance runs a single instance of the benchmark test to measure the speed of the system to perform a single task. rint runs the same number of instances of the benchmark test as there are threads in the machine to measure parallelization. Although a system may have a faster processor, other factors can reduce the number of parallel tasks, so rint is as important a measurement as cint. SevOne software provides good parallelization that benefits from more effective CPUs rather than from a smaller number of faster CPUs.
Example: A machine with two CPUs and four cores per CPU, with one thread per core, may have a speed rating of 10 and a throughput rating of 40, rather than 80, which would be the expected value if all cores and threads were completely independent so this machine has 4 effective CPUs. To expand further, consider a PAS10K which runs on Dell R620 hardware. There are 2 physical CPUs with 8 cores and hyperthreading is enabled. This should result in 32 effective CPUs, but the cint and rint values of 54.7 and 585 determine an effective CPU rating of almost 11, not 32. Similar results exist for the PAS200K (R720xd) which should have 40 effective CPUs but actually rates about 14.
Virtualization can provide better efficiency of the underlying hardware through a fundamental model of over subscription. When set up properly, VMs can freely move about within the cluster of hypervisors to resolve temporary resource constraints without administrator intervention. It is important to note the following:
-
Since the system may attempt to resolve resource contention issues autonomously, performance related postmortem analysis can be difficult via the VM alone.
-
From the VM, it is difficult to determine if you actually have the resources you think you have without an attempt to continuously allocate them, which degrades performance.
-
Some things that constrain the performance of VMs are not things that trigger a VM to move within the cluster.
-
Data points that describe the level of resource contention and over subscription are intentionally not revealed to the VMs and access to vCenter in those scenarios is not universal.
Troubleshooting System Performance
-
Ensure that CPU utilization is in the range of 50-70%. For VMs above this range, vCPUs must be added to the SevOne VM. Note that adding more vCPUs than necessary may adversely affect performance.
-
Ensure adequate reserve of CPU and memory for the VM. Through testing and experience, analyzing esxtop data, the appropriate level of reservation can be determined. Reservations only take effect when there are insufficient resources to meet the needs of all the VMs on a particular ESX server.
Multi Peer and Hot Standby Implementations
The SevOne NMS Cluster Manager provides an Integration tab to enable you to build your cluster and to add a new PAS appliance and/or a new vPAS as a peer into an existing cluster. The Cluster Manager also provides a Log Data Mapping tab to enable you to map the log data that SevOne PLA collects for volumes to the device groups/device types in SevOne NMS.
When your new virtual appliance is a Hot Standby Appliance, perform the steps in chapters 3 and 4 to install the SevOne software and to integrate the computer into your network then contact SevOne Support to ensure that the Hot Standby Appliance is appropriately implemented into the cluster. Email: support@sevone.com - Phone: +1 302-319-5400
Download Virtual Appliance OVA File
Perform the following steps to download the virtual appliance .ova image file from the SevOne download server.
-
In the Address field on your web browser, enter the virtual appliance image link from the email sent by SevOne.
-
Press Enter and wait for the following dialog to appear.
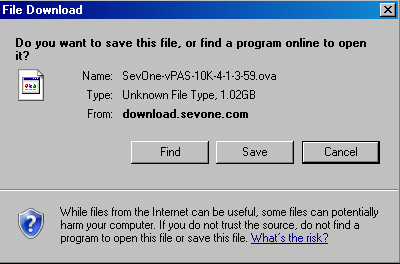
-
Click Save to display the Save As dialog.
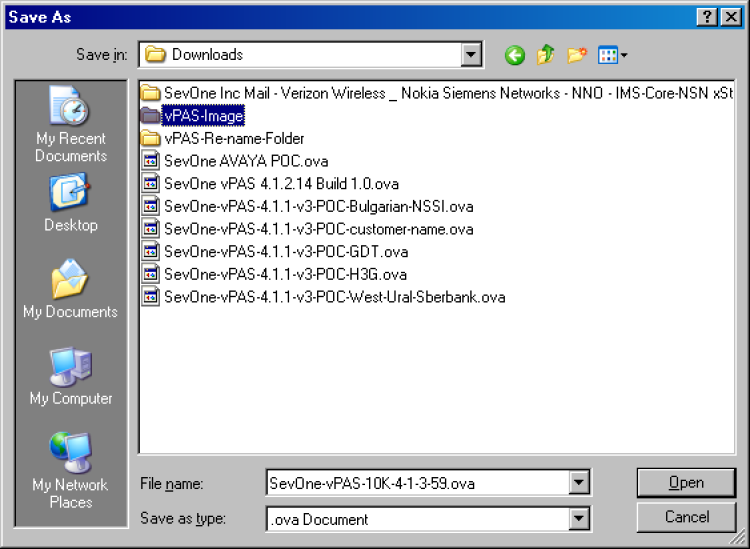
-
Navigate to the location in a local folder on your computer where you want to save the image.
-
Click Open to begin the download.
-
When the download is complete (can take up to 20 minutes), open your VMware vSphere Client. Your pages may vary from the following screen shots.
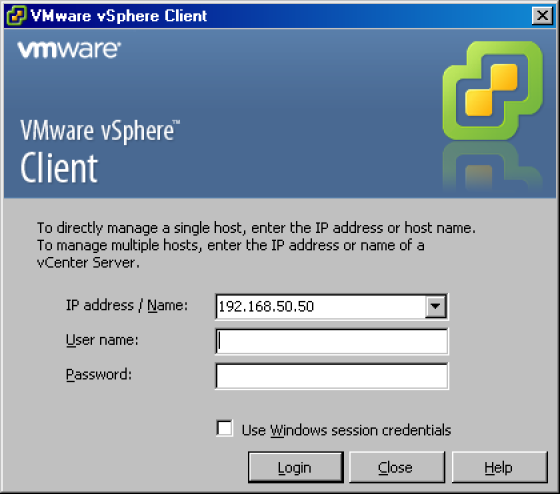
-
Login to your VMware vSphere Client to display the vSphere Client.
-
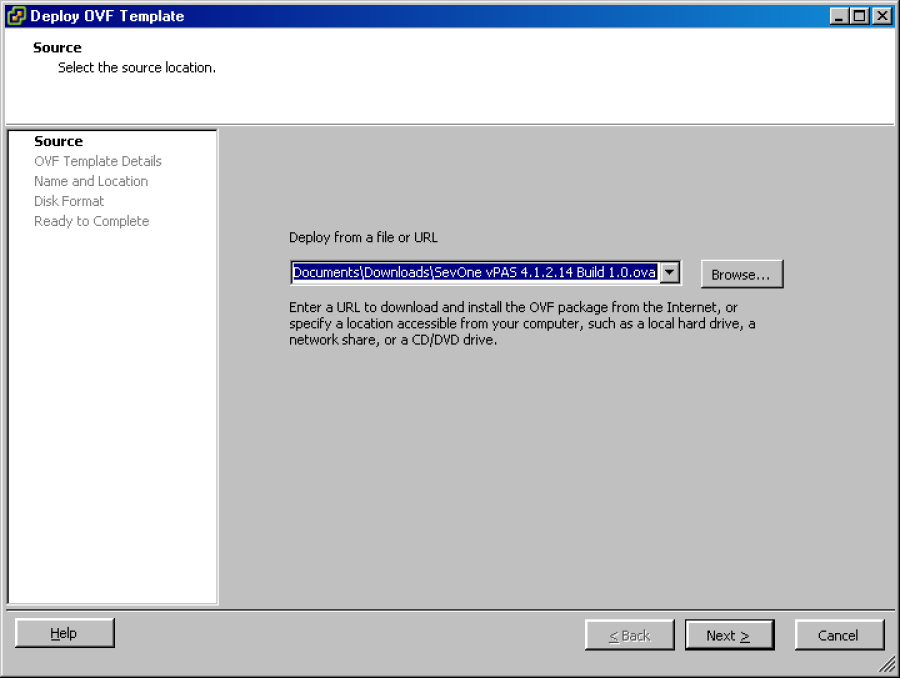
Click the File menu and select Deploy OVF Template to display the Source page on the Deploy OVF Template wizard.
-
Click Browse and navigate to the SevOne virtual appliance .ova file you downloaded.
-
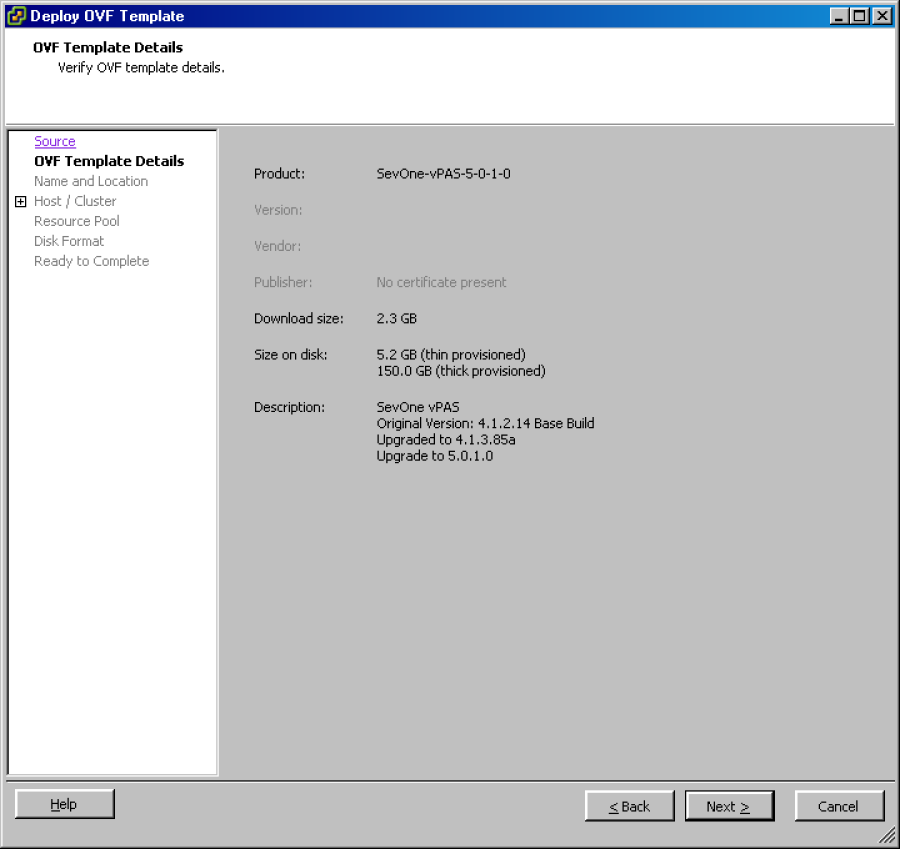
Click Next to display the OVF Template Details wizard page.
-
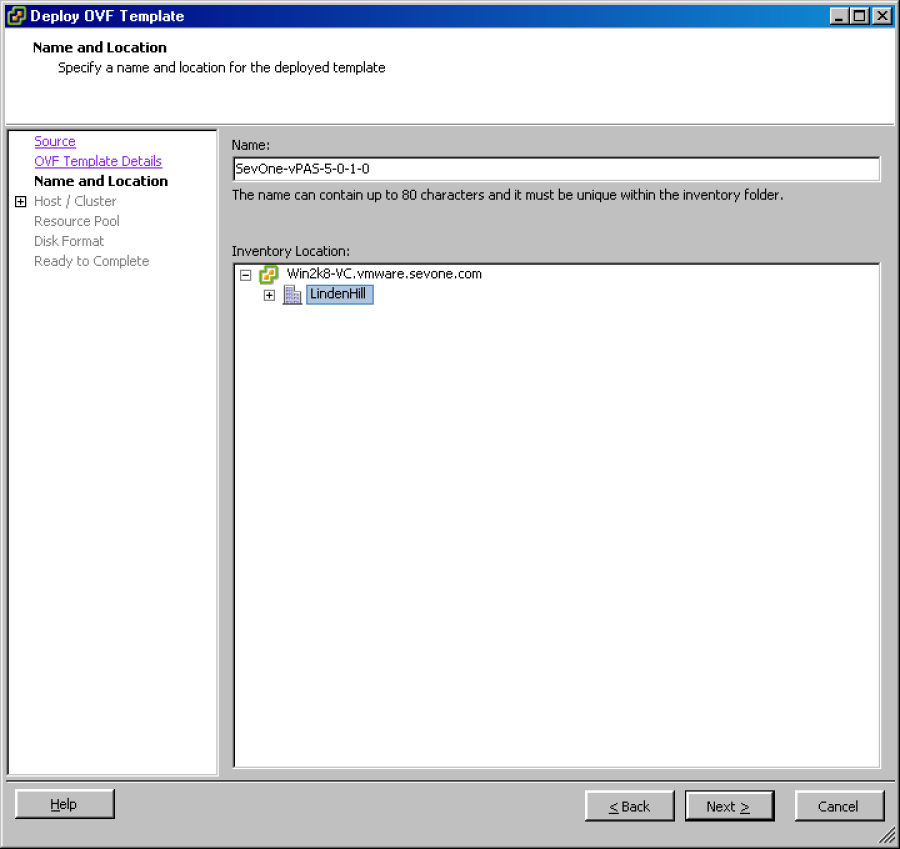
Click Next to display the Name and Location wizard page.
-
In the Name field, enter the name for the vPAS or vPLA.
-
In the Inventory Location field, navigate to the location for the vPAS or vPLA.
-
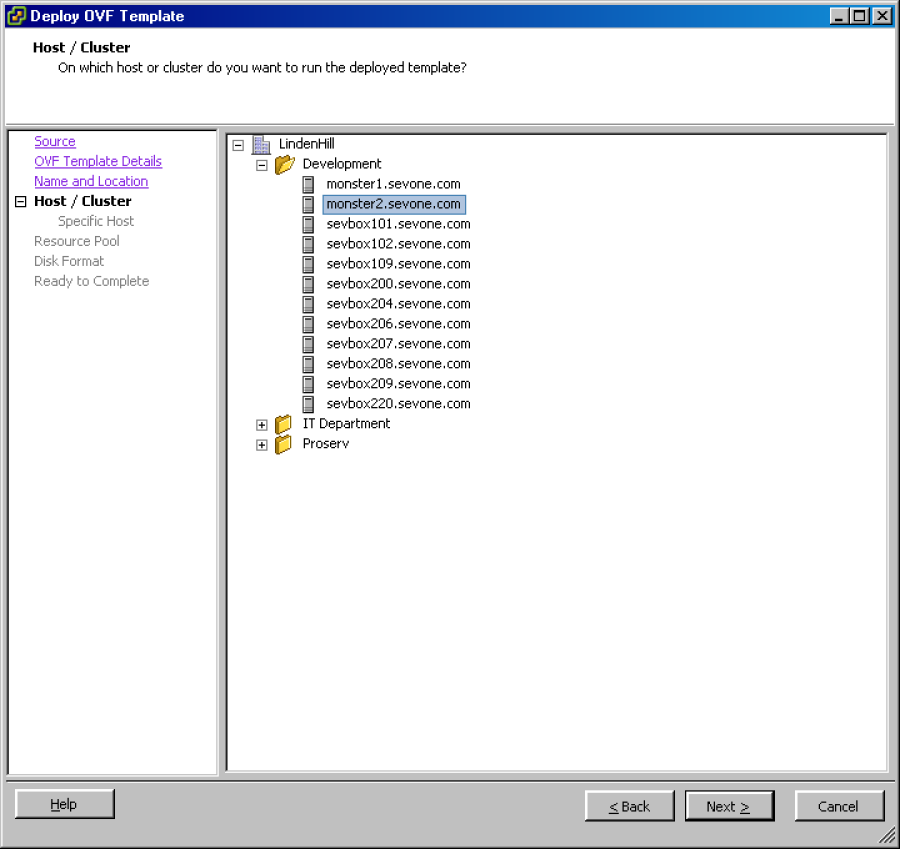
Click Next to display the Host/Cluster wizard page.
-
Select the cluster to host the vPAS or vPLA.
-
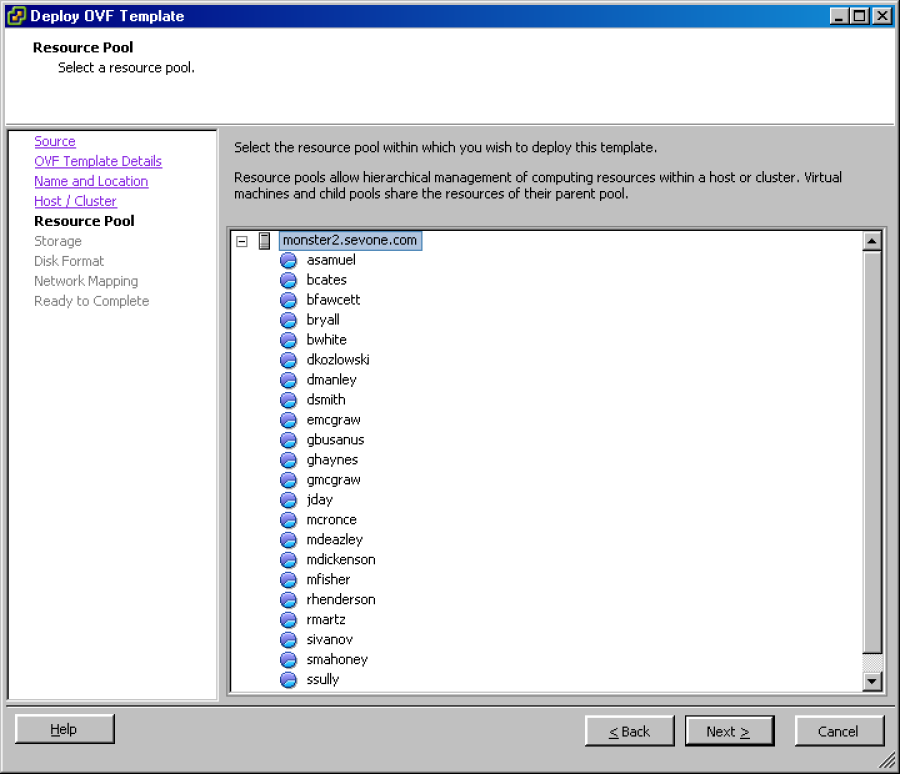
Click Next to display the Resource Pool wizard page.
-
Select the resource pool into which to deploy the vPAS or vPLA.
-
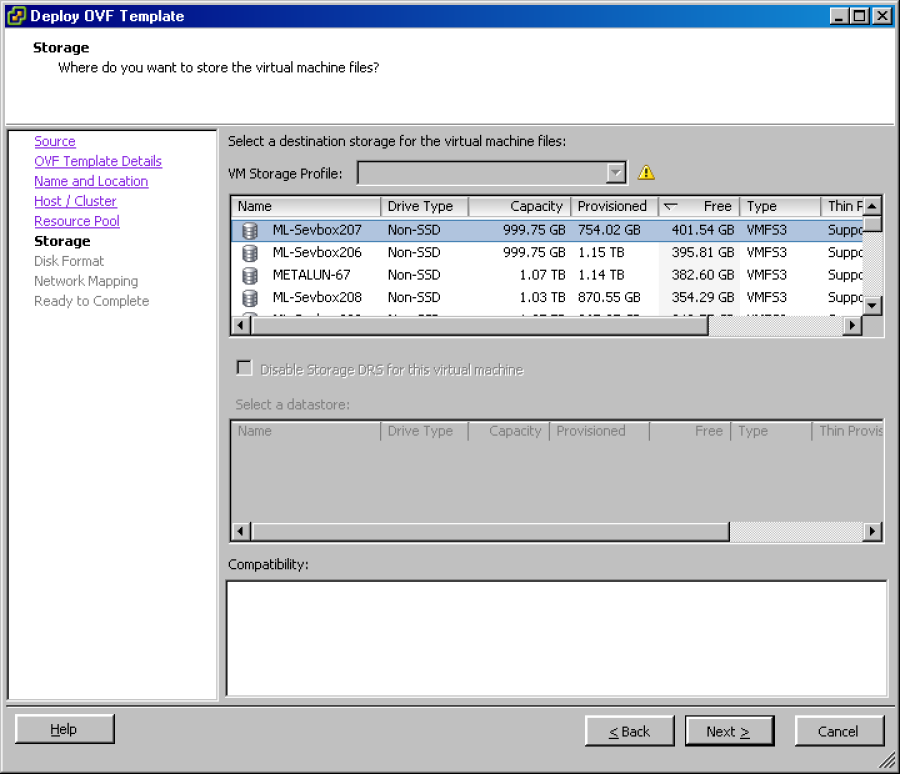
Click Next to display the Storage wizard page.
-
Select the destination for the vPAS or vPLA, (see the Prerequisites and Hardware Requirements chapter for required free space).
-
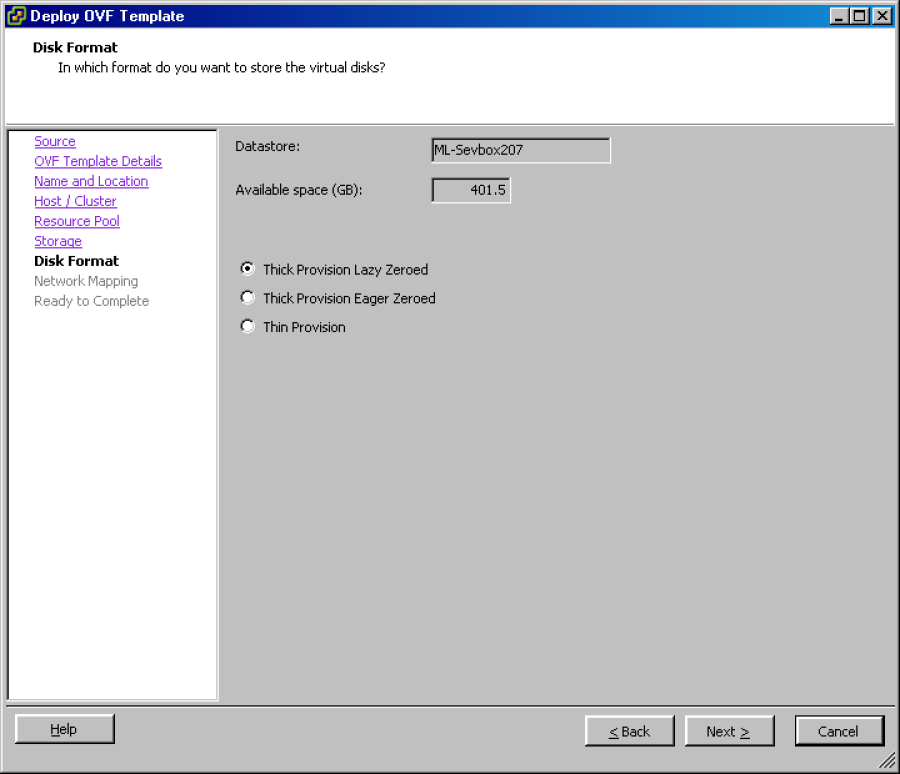
Click Next to display the Disk Format wizard page.
-
Leave the default settings and click Next to display the Network Mapping wizard page.
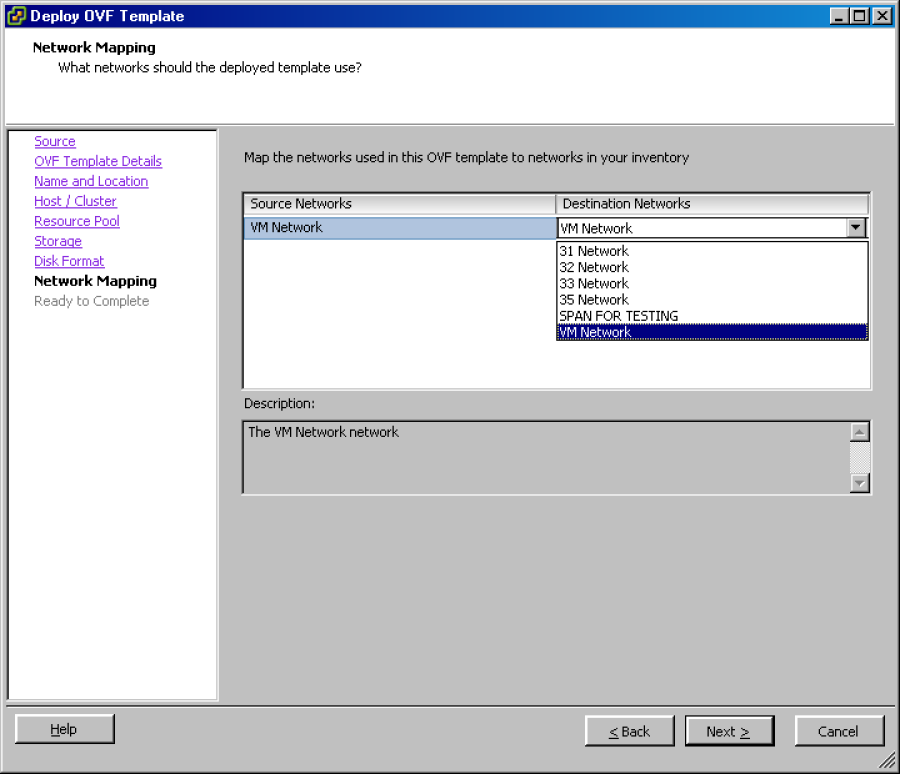
-
Click the Destination Network drop-down and select the destination network.
-
Click Next to display the Ready to Complete wizard page.
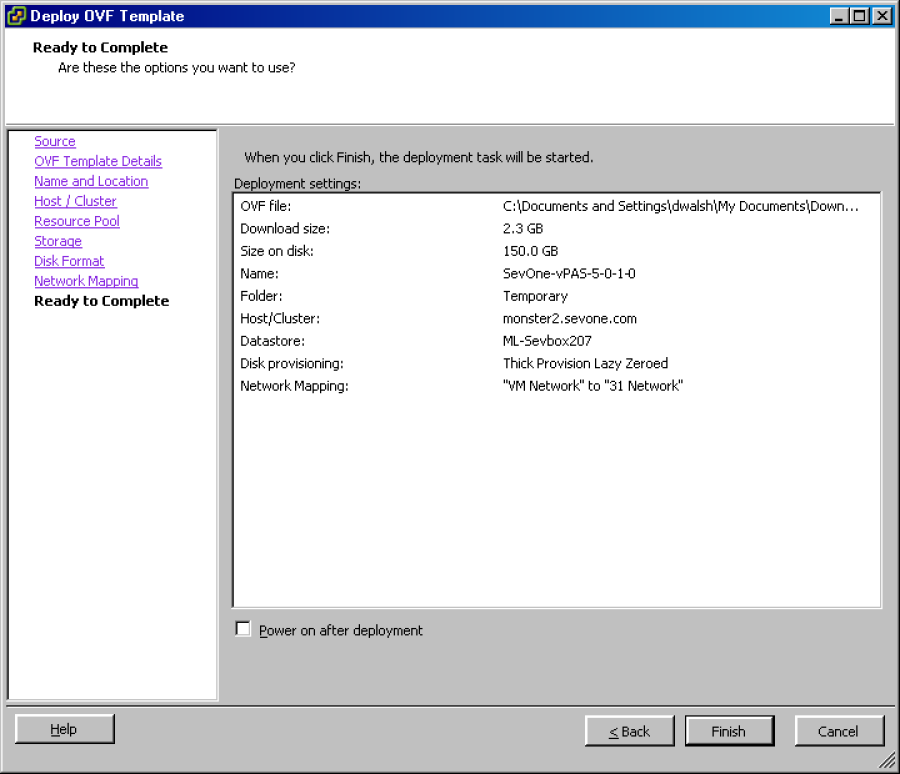
-
Select the Power on After Deployment check box.
-
Click Finish to display the Deploying status message.
-
Wait until the deployment is complete.
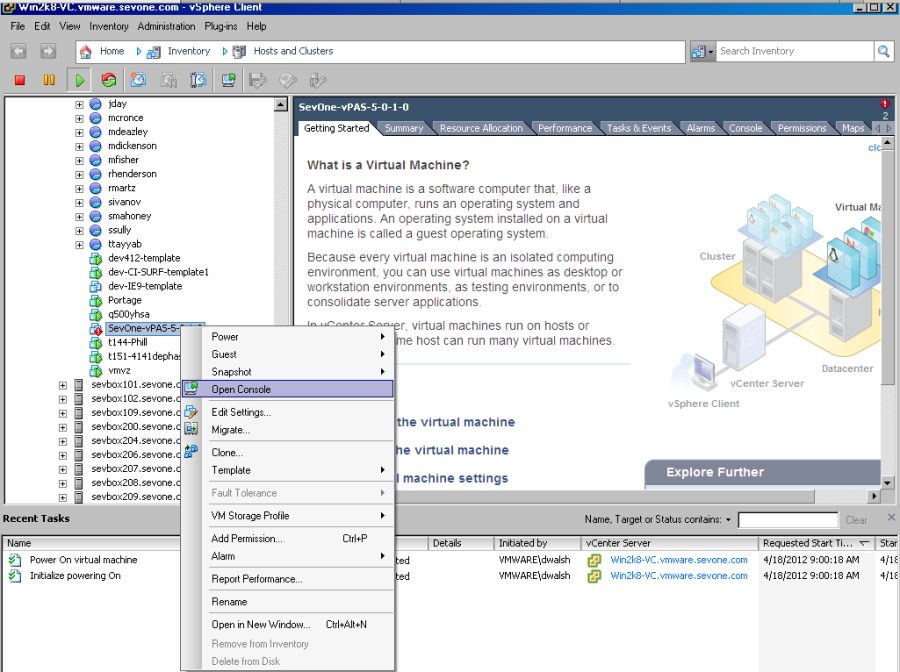
-
Right-click on the vPAS or vPLA and select Open Console to start the appliance network configuration.
Network Configuration
The following appears after you open the console on the SevOne NMS/SevOne PLA computer. From this point forward in the document, the SevOne NMS/SevOne PLA computer is referred to as the SevOne appliance. Use the configuration menu to enter your company's network settings. You need the following information:
-
System Name (Host Name)
-
Host IP address and sub-netmask
-
Broadcast address
-
Default Gateway IP address
-
DNS primary & secondary IP address
-
NTP (Time Server) IP address
-
SNMP Settings
-
Domain Name
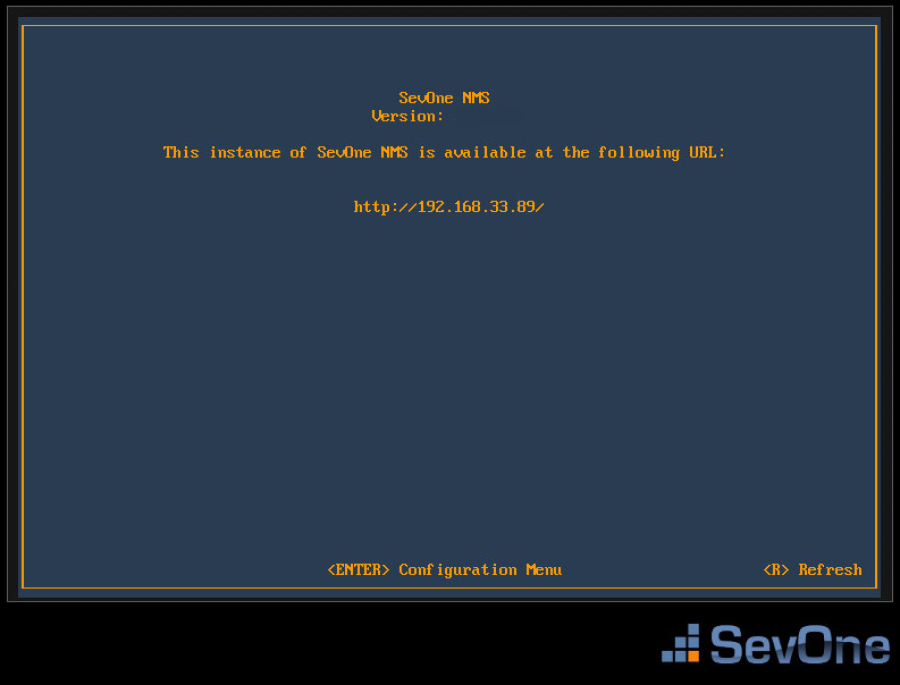
On the first page, press Enter to display the logon page that controls access to the Configuration Menu.
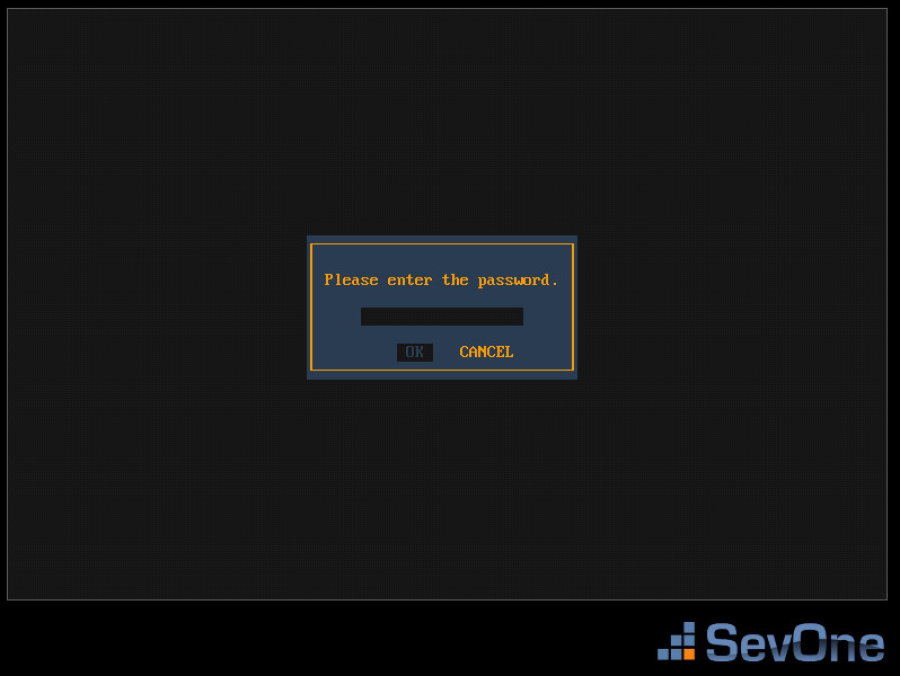
-
Enter the default password: changeme
-
Press Enter to display the system configuration menu.
With the Change Password option selected on the left, press Enter to display the Change Password fields on the right.
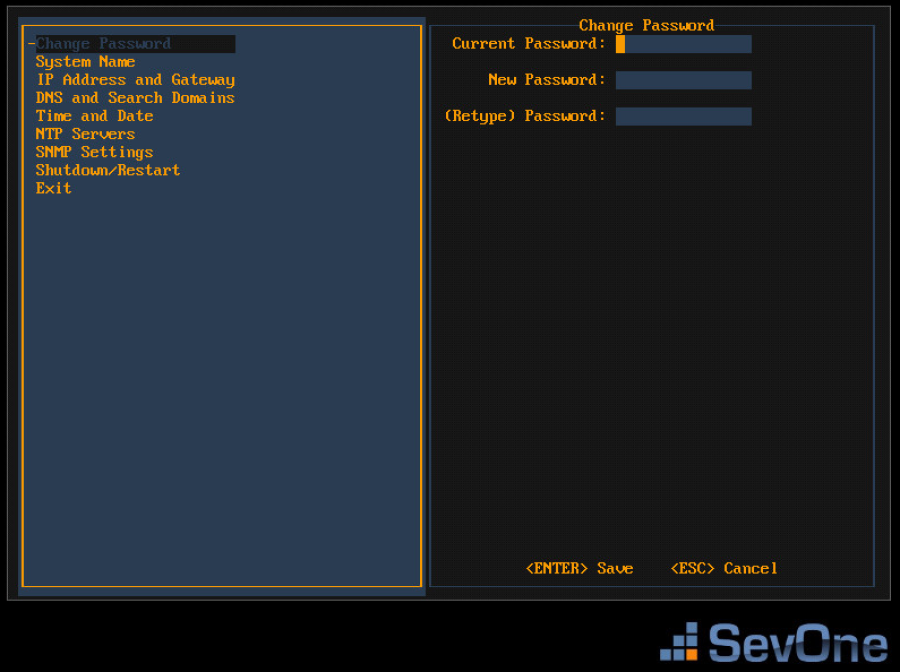
-
In the Current Password field, enter the current password (SevOne initial default password – changeme) and press Tab.
-
In the New Password field, enter your new password and press Tab.
-
In the (Retype) Password field, enter your new password a second time to confirm.
-
Press Enter to save the Change Password settings and return the focus to the menu on the left.
Press the down arrow to select System Name in the left menu and press Enter to display the System Name fields on the right.
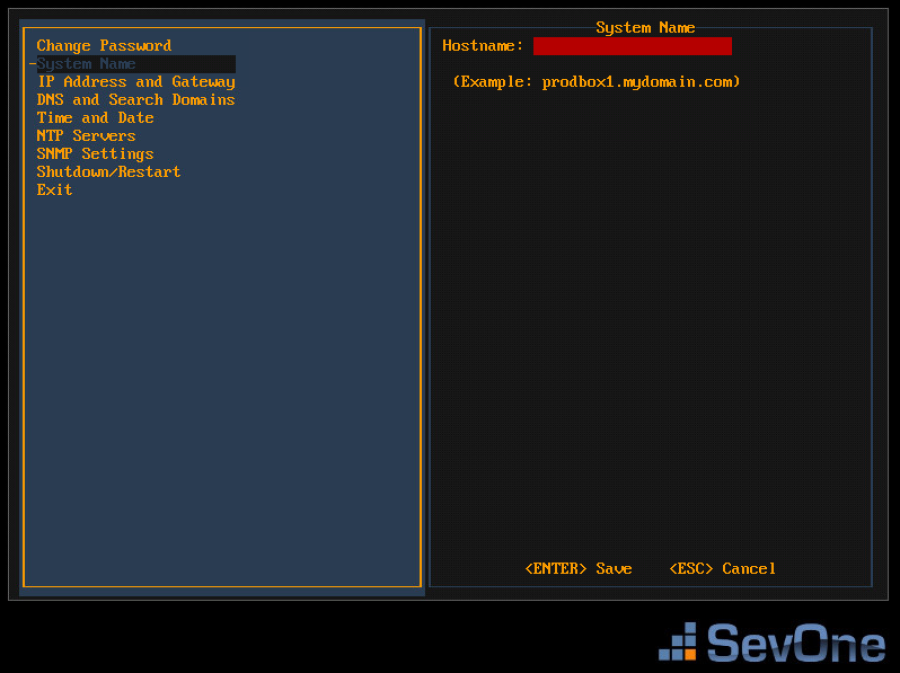
-
In the Hostname field, enter the hostname for the SevOne appliance.
-
Press Enter to save the System Name settings and return the focus to the menu on the left.
Press the down arrow to select IP Address and Gateway and press Enter to display the IP address and gateway fields on the right.
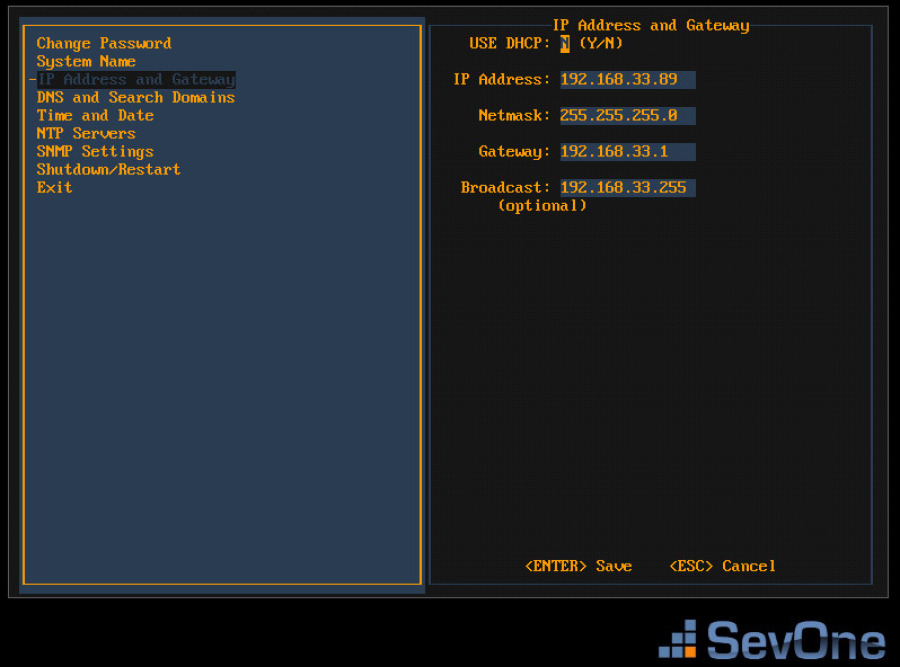
If your network uses DHCP type Y to disable the following fields and skip the IP Address and Gateway steps. If your network does not use DHCP, type N and complete the following fields.
-
In the IP Address field, enter IP address of the SevOne appliance and press Tab.
-
In the Netmask field, enter the netmask of the SevOne appliance and press Tab.
-
In the Gateway field, enter the IP address of the SevOne appliance and press Tab.
-
In the Broadcast field, enter the SevOne appliance broadcast IP address.
-
Press Enter to save the IP Address and Gateway settings and return the focus to the menu on the left.
Press the down arrow to select DNS and Search Domains and press Enter to display the DNS and Search Domains fields on the right.
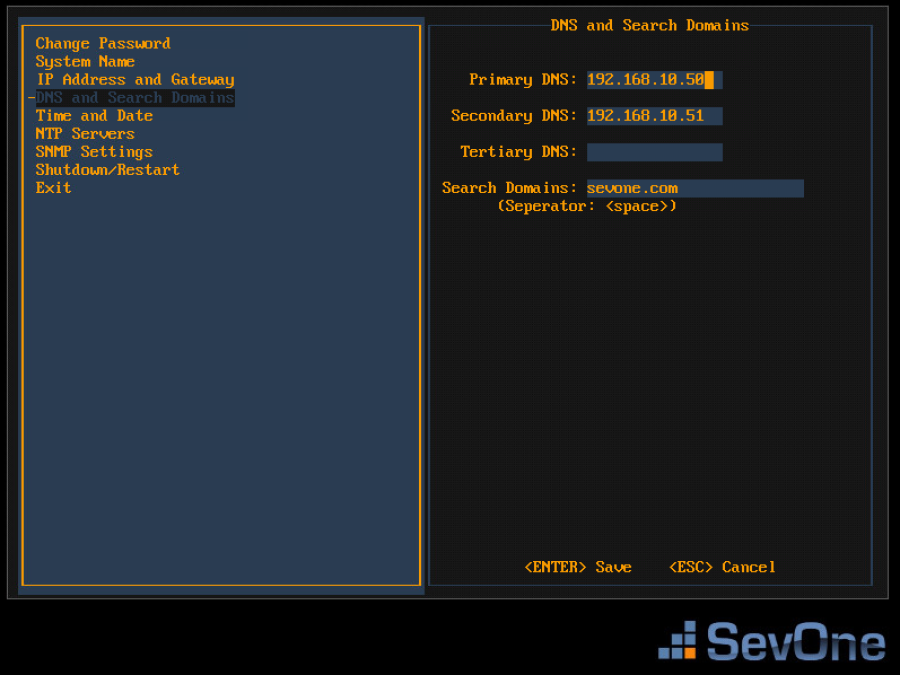
-
In the Primary DNS field, enter the IP address of the DNS server for the SevOne appliance to use first and press Tab.
-
In the Secondary DNS field, enter the IP address for the SevOne appliance to use second, if applicable and press Tab.
-
In the Tertiary DNS field, enter the IP address of the DNS server for the SevOne appliance to use third, if applicable and press Tab.
-
In the Search Domains field, enter the domain names or IP addresses for the search domains for the SevOne appliance to use (separated by a space).
-
Press Enter to save your DNS and Search Domains settings and return the focus to the menu on the left.
Press the down arrow to select Time and Date and press Enter to display the Time and Date fields on the right.
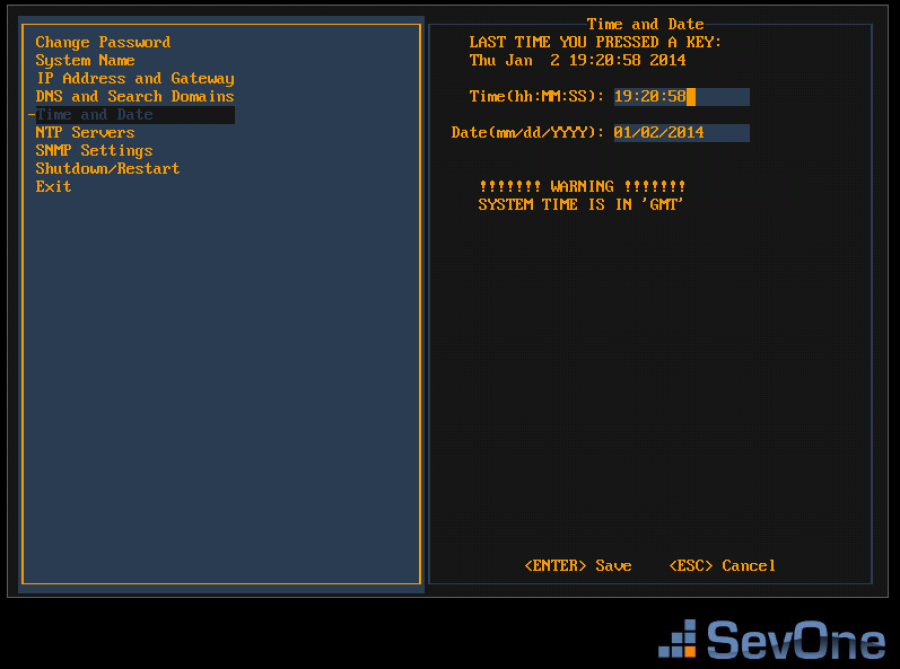
-
Confirm that the time and date are correct for Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) (a.k.a. Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)). This is the SevOne NMS/PLA system time. You define time and date settings for users, devices, and reports via the SevOne NMS/PLA GUI in a later step.
-
If needed, enter the time and date using the appropriate format in the fields provided.
-
Press Enter to save the Time and Date settings and to return the focus to the menu on the left.
Press the down arrow to select NTP Servers and press Enter to display the NTP Servers fields on the right.
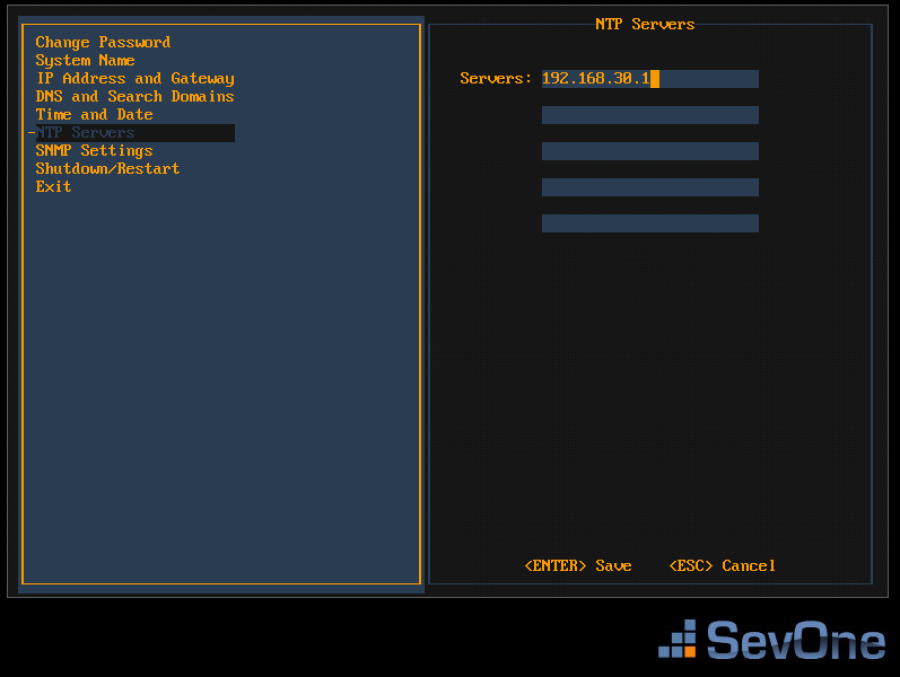
-
In the Servers field, enter the DNS name or IP address of the time server for the SevOne appliance to use to maintain time settings.
-
Press Enter to save the NTP Servers settings and to return the focus to the menu on the left.
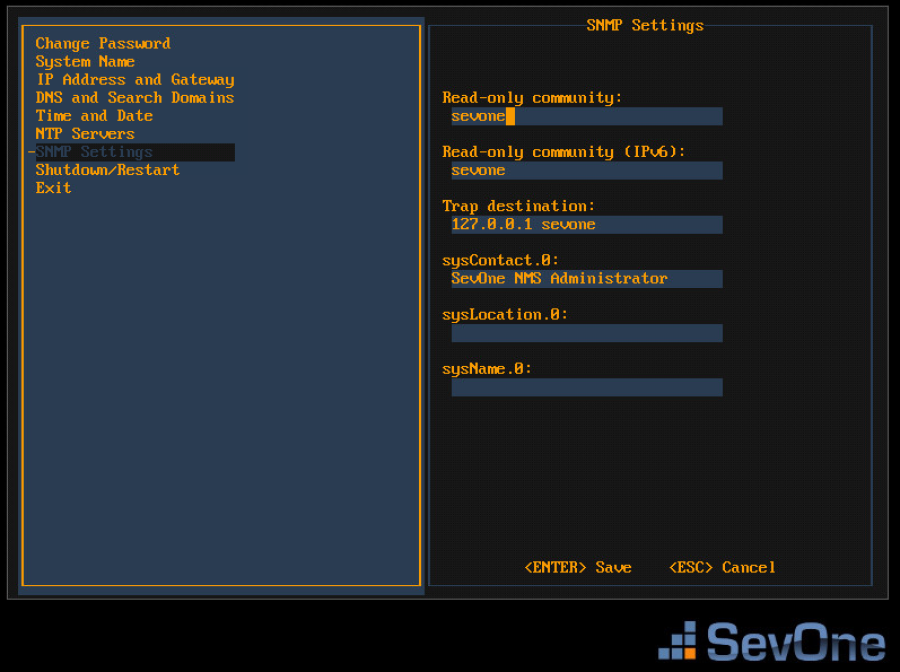
Press the down arrow to select SNMP Settings and press Enter to display the SNMP Settings fields on the right.
-
In the Read Only Community field, enter the SNMP read community string for other devices to use to poll SNMP data on the SevOne appliance when communicating via IPv4 and press Tab.
-
In the Read Only Community (IPv6) field, enter the SNMP read community string for other devices to use to poll SNMP data on the SevOne appliance when communicating via IPv6 and press Tab.
-
In the Trap Destination field, enter the IP address or hostname of the destination where traps the SevOne appliance generates are to be sent and press Tab.
-
In the sysContact.0 field, enter the text you get when you SNMP walk the sysContact OID and press Tab.
-
In the sysLocation.0 field, enter the text you get when you SNMP walk the sysLocation OID and press Tab.
-
In the sysName.0 field, enter the text you get when you SNMP walk the sysName OID.
-
Press Enter to save the SNMP Servers settings and to return the focus to the menu on the left.
If you changed the System Name settings or the IP Address and Gateway settings, press the down arrow to select Shutdown and Restart and press Enter to display a Shutdown option and a Restart option on the right.
For all other configuration setting changes, you can press the down arrow to select Exit.
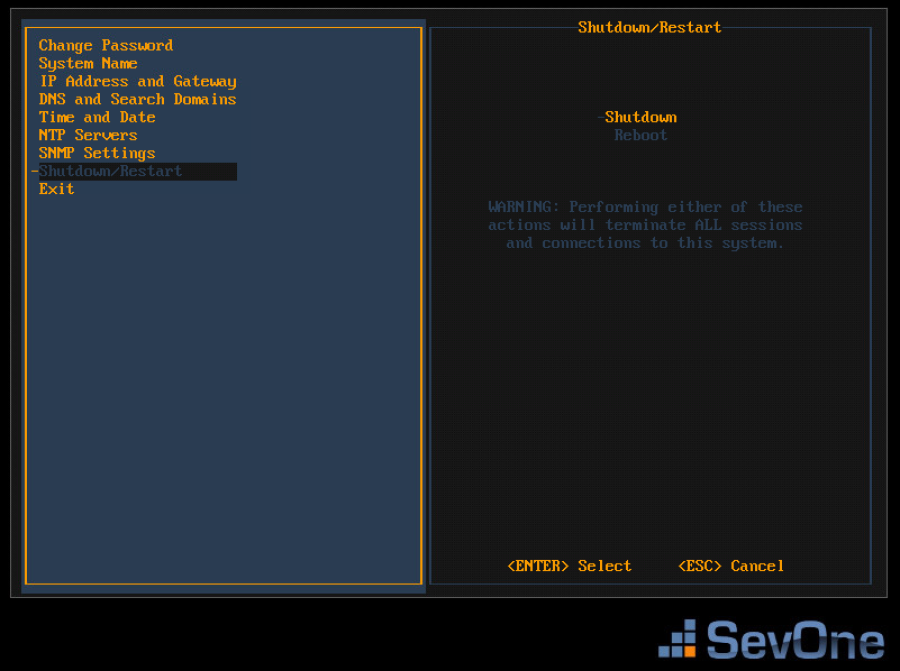
In the Shutdown/Restart section select an option and press Enter to shut down or reboot the SevOne appliance.
If you highlight Exit, when you press Enter the initial Configuration Menu Welcome page appears.
Install vPAS License File
Your license file is attached to the email.
-
Save the <license>.dat file to a location that is accessible by the SevOne appliance.
-
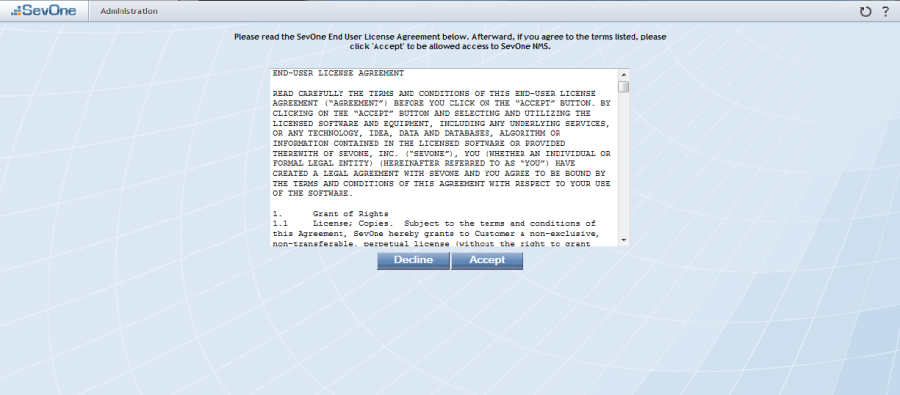
Enter the URL for the SevOne appliance into your web browser to display the license agreement.
-
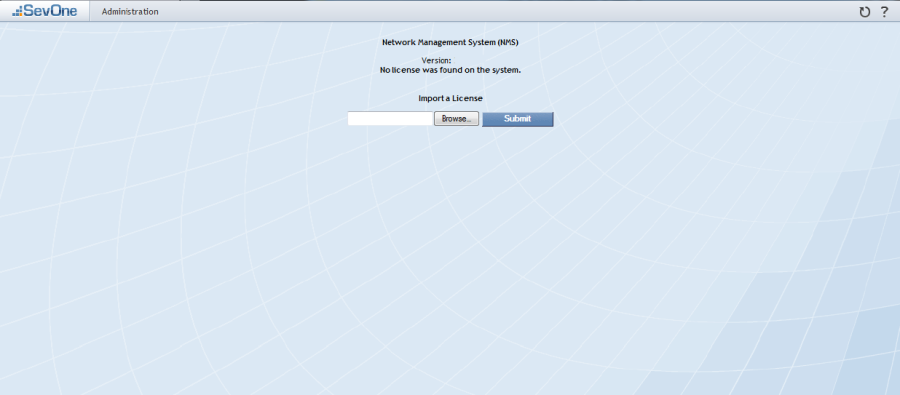
Click Accept to display the License Upload page.
-
Click Browse.
-
Navigate your file hierarchy to the license.dat file, select the <license>.dat file, and click Open.
-
Click Submit to import the license.
-
On the Finish Importing Certificate message, click OK.
-
Restart your browser.
SevOne PLA Email Server Setup
Perform the following steps to define the email server for the SevOne PLA to use to send report and alert emails. For SevOne NMS, skip this section.
-
From the command line, enter the following command to display the current email server settings:
set-email-server -
Enter the following to keep the current settings:
^C -
When prompted, enter the URL for the mail server.
-
When prompted, enter the username for the mail sender.
-
Enter the password for the sender to connect to the server (or leave blank for no password).
-
Enter the email address from where emails are to be sent.
Add a SevOne PLA to a SevOne NMS Cluster
Perform the following steps to include the SevOne PLA in a SevOne NMS cluster.
Generate Token
You can enter the following command on the SevOne PAS appliance to generate a token for the PLA appliance.
wget http://<PLA Appliance IP Address>/rapid/req.php --post-data-data='{"action": "request-superadmin-action-tokens", "user":"admin", "pass":"test" }' -qO-
To avoid sending credentials over the wire, you can enter the following command on the PLA appliance. Substitute localhost for the IP address.
wget http://localhost/rapid/req.php --post-data='{"action": "request-superadmin-action-tokens", "user":"admin", "pass":"test" }' -qO-
Sample Return:
{"tokens":{"function":"get-mass-volume-info","token":"kNHtKMSisibA0tvpBXVt"}}
Store Authentication Token and PLA IP Address in the SevOne-act
Enter the following command on the SevOne PLA appliance.
SevOne-act pla init-set-pla --ip <PLA Appliance IP Address> --token <Token>
Shut Down and Reboot SevOne NMS
SevOne NMS can run for extended periods of time. Occasionally it is necessary to shut down or reboot an appliance. SevOne NMS stores data in cache and writes to the disk on a regular basis.
The following shell commands back up the memory ring tables to the database on the disk to ensure that you do not lose data.
To shut down SevOne NMS:
SevOne-shutdown shutdown
To reboot SevOne NMS:
SevOne-shutdown reboot